小组成员余小于的论文被 ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing(一区top,IF=12.7)接收
- 日期:2024-02-28

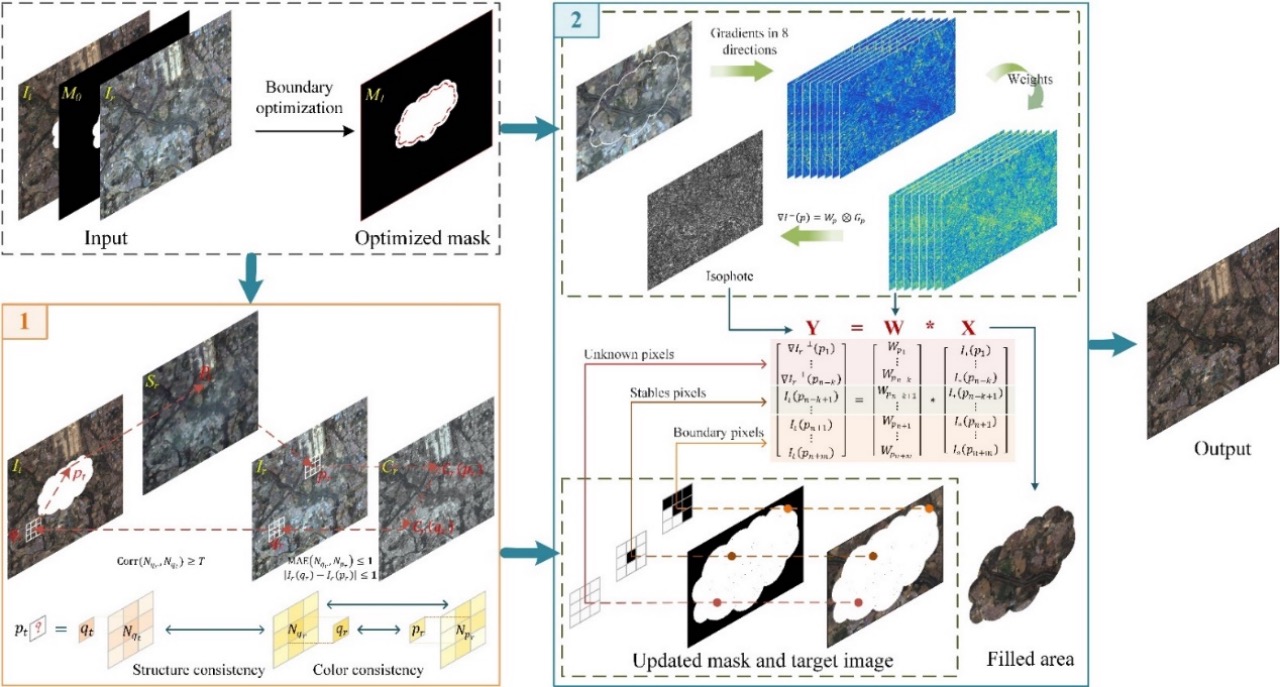
Abstract—Remote sensing imagery usually suffers from information loss issues due to the sensor defects and harsh atmospheric conditions, resulting in a significant decrease in data quality. In light of this, a novel image reconstruction method is proposed to improve the usability of such data. The proposed method uses the isophote information in reference image as constraint to recover the missing information in target image. Isophote refers to the neighboring pixels with same illumination intensity, that is, the pixels with similar gray values. The adaptive weighted gradient is put forward to calculate the isophote of a pixel. Due to the greater weight in the direction of minimum gradient, the difference between similar pixels in image tends to remain constant to minimize the isophote difference between images. As a result, in the reconstructed image, radiometric differences between reference image and target image are attributed to areas where pixel values change significantly, and the pixels belonging to same ground feature will have similar values, thereby ensuring the internal stability of the feature and increasing the variance between different features. Furthermore, to control the color fidelity of ground features and improve the reconstruction accuracy, the target image is updated with certain pixels before isophote-based image reconstruction. These pixels are filled with the auxiliary information outside the missing area under color-structure control, and evenly distributed in each uniformly colored small zone of the missing area. Experiments under different missing information cases have demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed method, and the experimental results indicate that the proposed method can obtain visually reasonable images with high color consistency and reconstruction accuracy even for images with large missing areas. The source code of this work is available at https://github.com/YuXiaoyu221/IC_CSC-Information-Reconstruction.